There can be your advertisement
300x150
Wall Insulation with Polystyrene Foam
Energy prices on today's market are incredibly high. This fact increases the importance of using energy-saving technologies during the construction of any heated building, which help reduce heating and air conditioning costs throughout the year. There are now many such technologies.
One of the oldest and most widespread methods is insulation using expanded polystyrene beads.
Although in most countries polystyrene is used only as packaging material, for example, for household appliances or antiques (in granular form), in Ukraine it has long occupied a leading position as the most popular insulating material. Polystyrene is used for insulating walls and flat roofs, floors under screed, and foundations. This article focuses on insulating building envelope components with polystyrene boards.

Three-layer Wall Construction
The most common structural solution for external building envelopes using polystyrene is a three-layer wall. This wall structure is built entirely or partially from small masonry units (brick, lightweight concrete block, stone, ceramic block). The polystyrene layer is placed between the outer and inner wythes, forming a multi-layered structure.
The inner and outer brick courses are interlocked using flexible ties or reinforcing mesh with a spacing of 0.6 to 1.2 meters. In the first case, polystyrene boards are slipped onto pre-installed ties in the inner wythe; in the second, they are positioned so they rest on the reinforcing mesh.
When implementing a three-layer wall, polystyrene boards are inserted into the wall parallel to the construction process. Thus, this structural solution allows polystyrene use only in new construction. However, for reconstruction of old, uninsulated buildings, polystyrene can be used in a wet-rendered facade system.
Rendered Wet Facade System
The most common method for upgrading facades of old buildings, including those with historical value, is the installation of a rendered wet facade. This method improves energy efficiency, preserves the original architectural appearance, and extends the lifespan of deteriorating walls.
The principle involves first attaching polystyrene or mineral wool panels to the wall. Attachment is performed using a cement-based adhesive. After 24 hours, the insulation material is further secured at five points per board using special flat-head anchors.

Next, the polystyrene is coated with a priming and adhesive compound, into which a polymer-reinforced mesh is embedded. On the final stage, a decorative cement-based render is applied over the multi-layered structure.
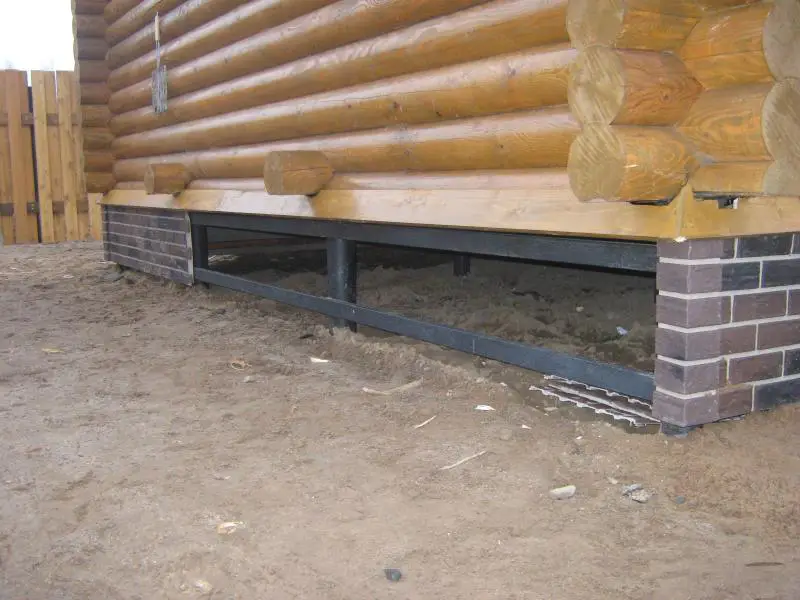
Insulation of Subsurface Wall and Foundation Parts
Polystyrene is nearly inert to moisture, so it can be used below ground level. The material is bonded to a bituminous waterproofing coating, which covers subterranean wall and foundation sections. Although additional fastening is not required, in certain cases it may be secured at one or two points using the same flat-head anchors.
A good alternative to expanded polystyrene in foundation construction is extruded polystyrene, which differs from traditional polystyrene by its closed-cell structure, enhancing thermal insulation and mechanical strength.