Foundation Insulation
Often, after spending considerable money, effort, and time on building a strong, well-buried foundation for their home, clients overlook a relatively minor component: foundation insulation. Many homes are built with a basement, either fully or partially located below ground level.
Often, after spending considerable money, effort, and time on building a strong, well-buried foundation for their home, clients overlook a relatively minor component: foundation insulation.
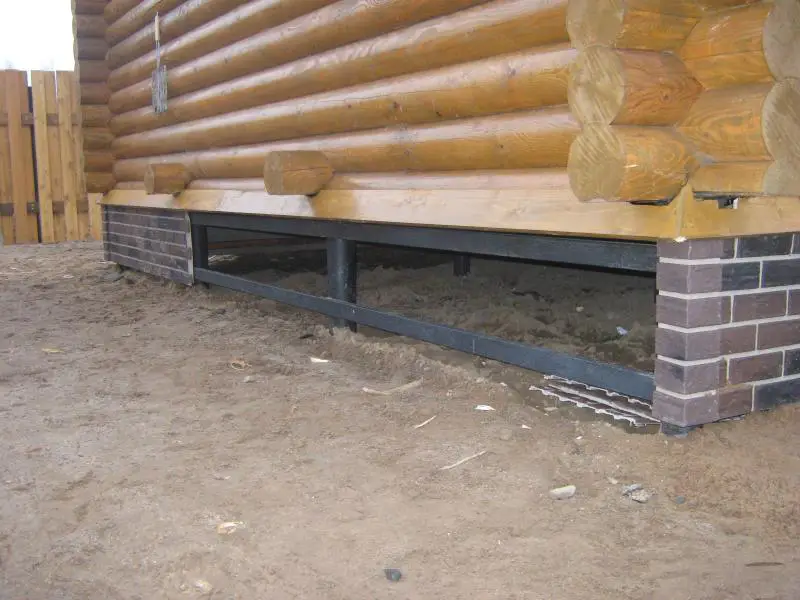
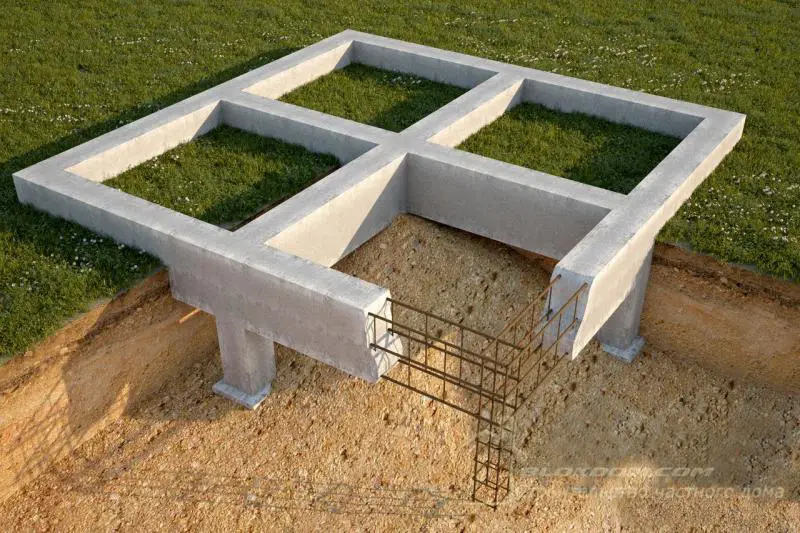
Many homes are built with a basement, either fully or partially located below ground level. In such cases, insulation can prevent serious consequences from through-freezing of blocks or concrete footings. However, even if a home does not have a basement or cellar, this does not mean the foundation can remain uninsulated.
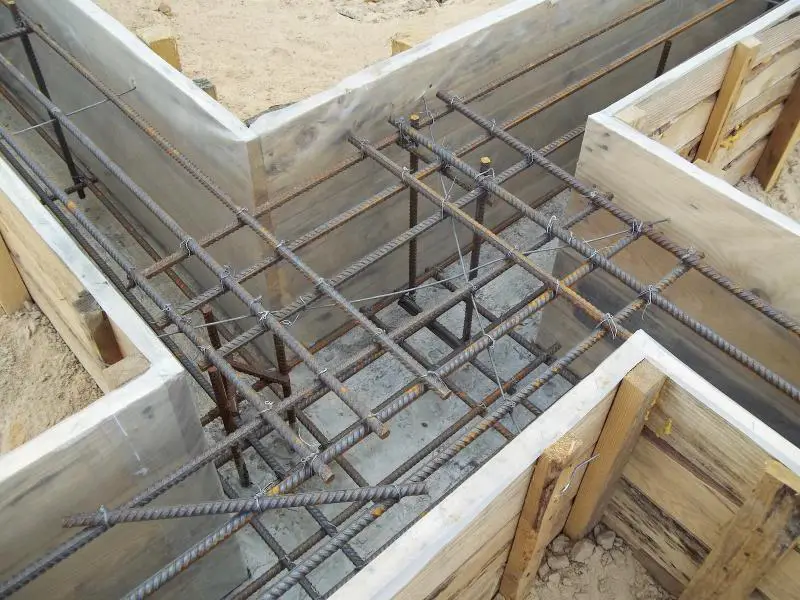
According to statistics, the foundation typically accounts for 15–17% of the total construction budget for a private home under normal conditions. That’s no small expense. The durability of concrete, whether in a monolithic strip or in FBS blocks, directly depends on how many freeze-thaw cycles the material has endured. External insulation attached to the foundation keeps the concrete base constantly in a positive temperature zone, significantly increasing the foundation's lifespan.

Insulation Technology
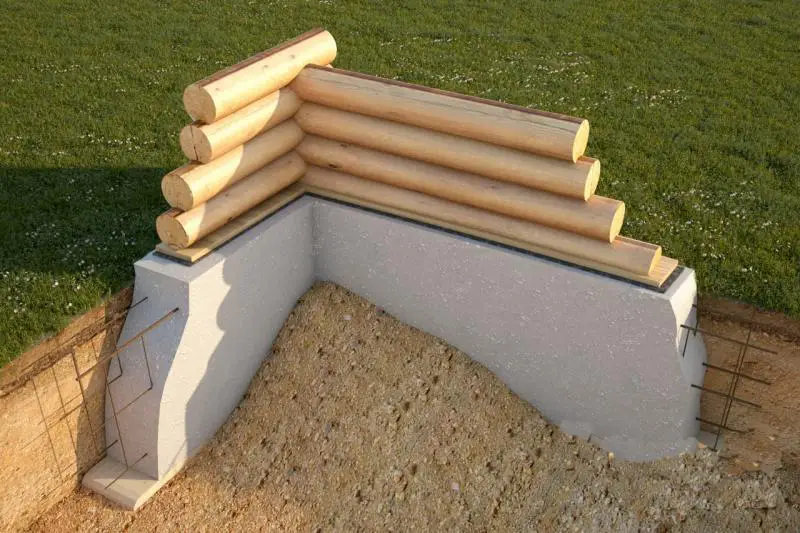
Foundation insulation uses one of the most practical and effective thermal insulators available today: extruded polystyrene. This material is produced via extrusion (extrusion) of styrene-based raw material through a specialized die. The blowing agent used is either freon or carbon dioxide.
Extruded polystyrene boards come in various sizes and thicknesses, but the most common size in general construction is 600 x 1200 mm, with thicknesses ranging from 30 to 100 mm. The material has an exceptionally low thermal conductivity (0.029 W/mK), allowing for thin application. Most manufacturers produce extruded polystyrene with offset edges to prevent thermal bridging.
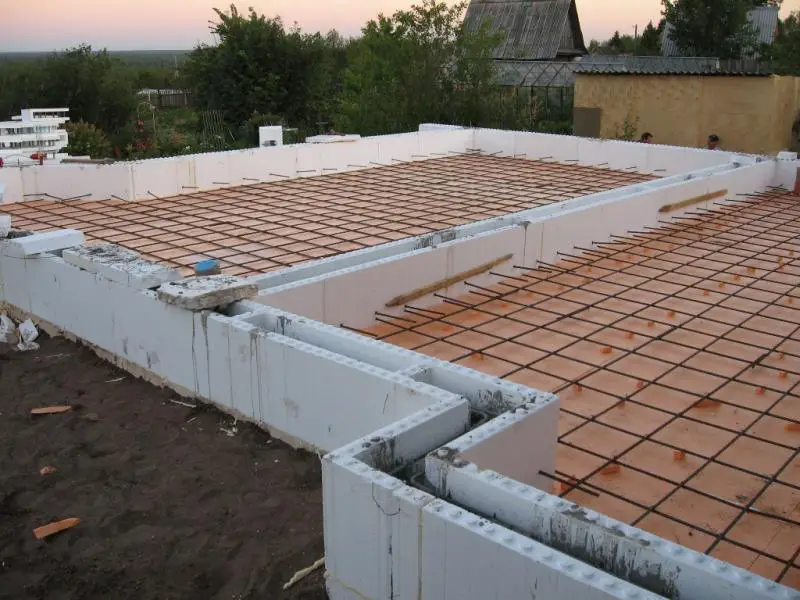
Insulation is applied externally to the foundation using polystyrene boards fixed with disc-shaped anchors over a coating-type waterproofing layer. The insulation thickness is determined by calculation based on regional climate, degree-days of the heating period, intended use, and temperature regime of the basement. All these factors are directly or indirectly considered during thermal engineering calculations.
Further finishing of the polystyrene portion above ground level can vary widely—from simple plastering to using decorative panels made of natural stone. Polystyrene is a durable and practical thermal insulator, also used for insulating concrete pads under the foundation.
Since the compressive strength of extruded polystyrene can exceed 700 kPa, it is ideal for use under concrete pads, blocking cold air from below—especially critical in northern regions where soil freezing depths are significant.
Need a renovation specialist?
Find verified professionals for any repair or construction job. Post your request and get offers from local experts.