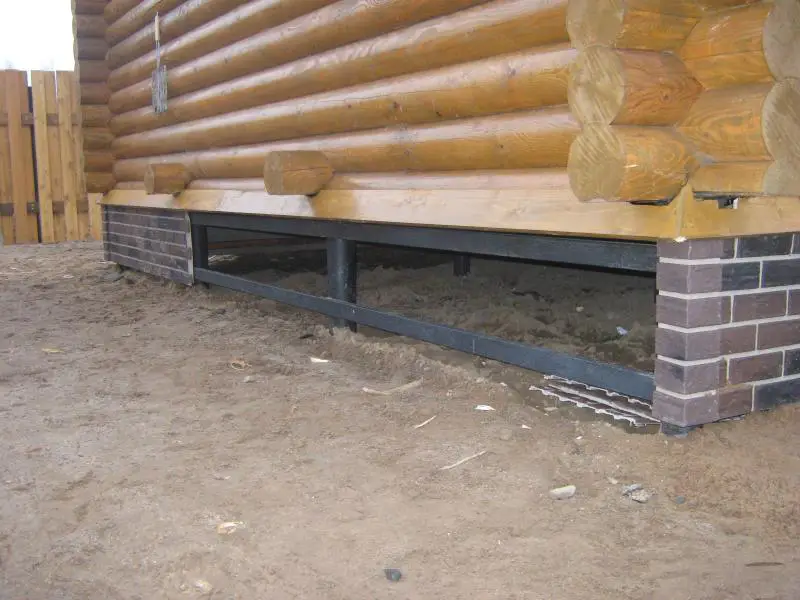
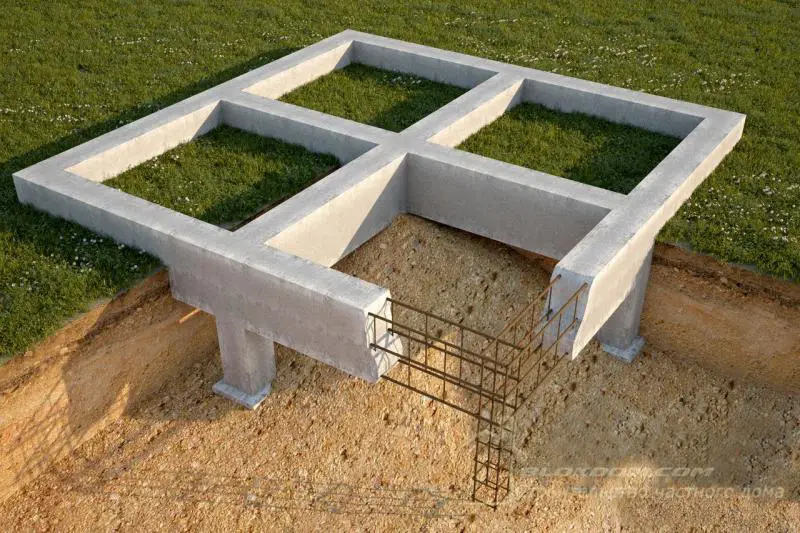
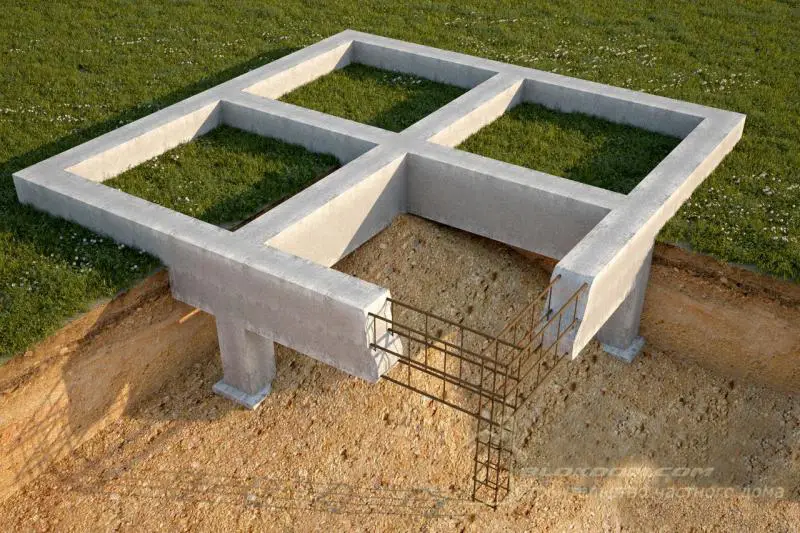
Which rebar to use for a foundation
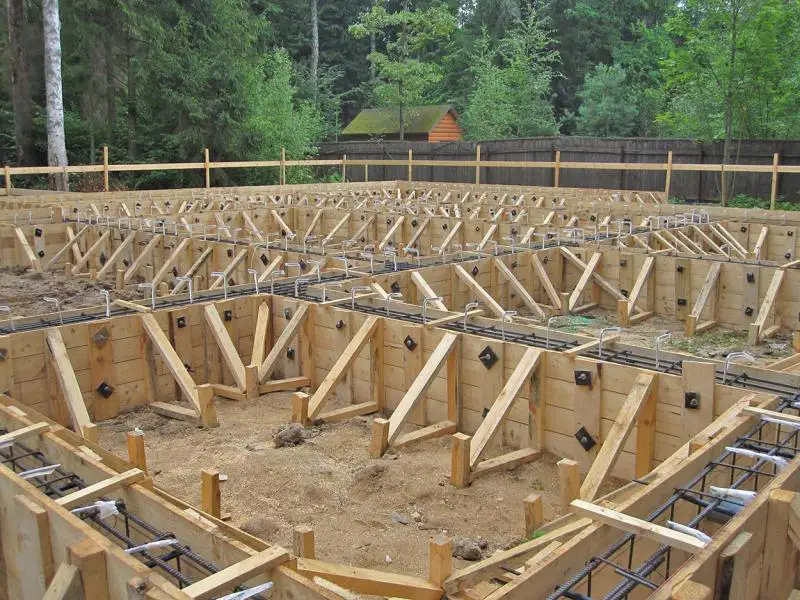
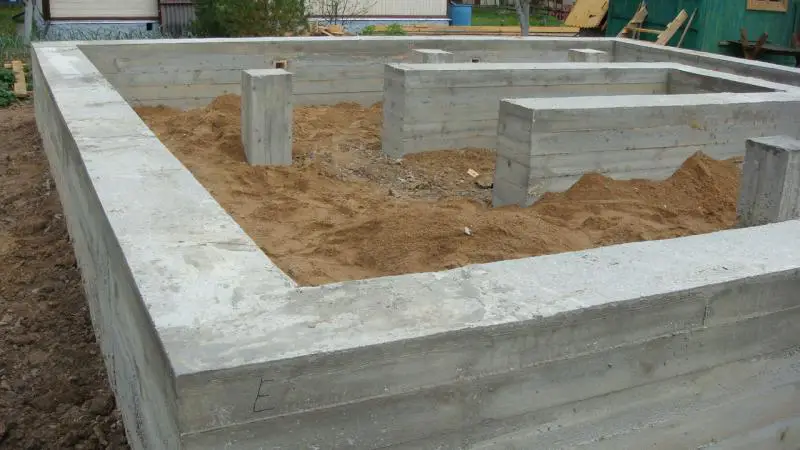
In every construction, a properly laid foundation plays a crucial role, as its quality directly determines the reliability and durability of the structure. To ensure foundation reliability, it’s essential to choose the right type based on local terrain conditions and materials used in its construction. Among these materials, rebar is a key component, forming connections between individual foundation elements and creating the structural framework of the foundation itself.
The strength of the foundation largely depends on the quality of the selected rebar. Therefore, let’s examine in detail which type of rebar should be used when constructing a foundation.
Choosing the rebar grade
For reinforcing the future foundation’s framework, hot-rolled, smooth, rod-shaped rebar of class A1, grade A240, is commonly used. However, this type is not recommended as a primary structural material due to its poor bond with concrete.
Primary structural rebar includes grades A2, A3, A4, A5, and A6, each with their respective markings. These grades consist of hot-rolled, rod-shaped rebar with a surface featuring a "braid" pattern with a periodic profile. This design ensures excellent adhesion to concrete mix, and additionally, provides strong resistance to both tension and compression.
Rebar marked with the letter "C" can be used for welding, while rebar labeled "K" offers enhanced resistance to corrosion.

Choosing the rebar cross-section
Foundation rebar is manufactured using round steel, either smooth or with a periodic profile. The periodic profile features a textured pattern at an angle to the rod’s axis, designed to improve concrete bonding with the surface layers of the rebar.
A key performance characteristic of foundation rebar is the periodic spacing of surface protrusions. The smaller the distance between these protrusions, the more securely the rebar will bond within the concrete.
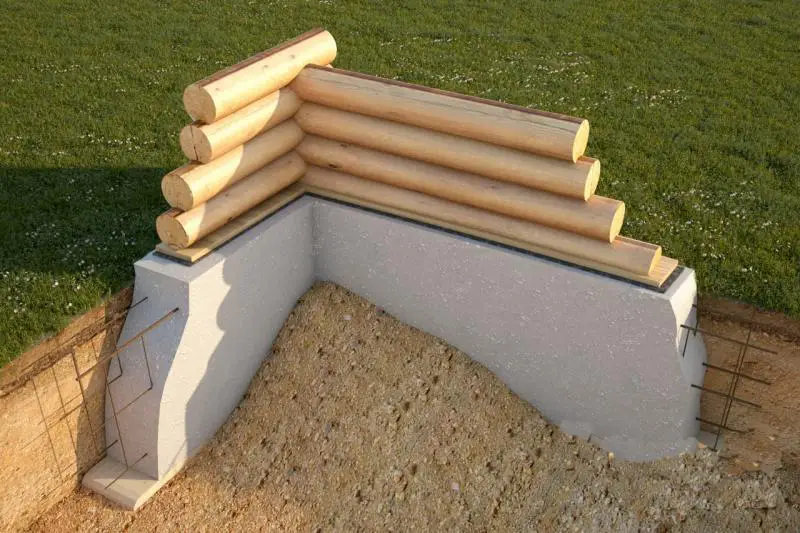
The most critical parameter for foundation rebar is its diameter. For standard residential buildings, rebar with a diameter of 10–12 mm is typically used. For larger, more massive residential structures, 14 mm diameter rebar is recommended.
Using prefabricated rebar assemblies
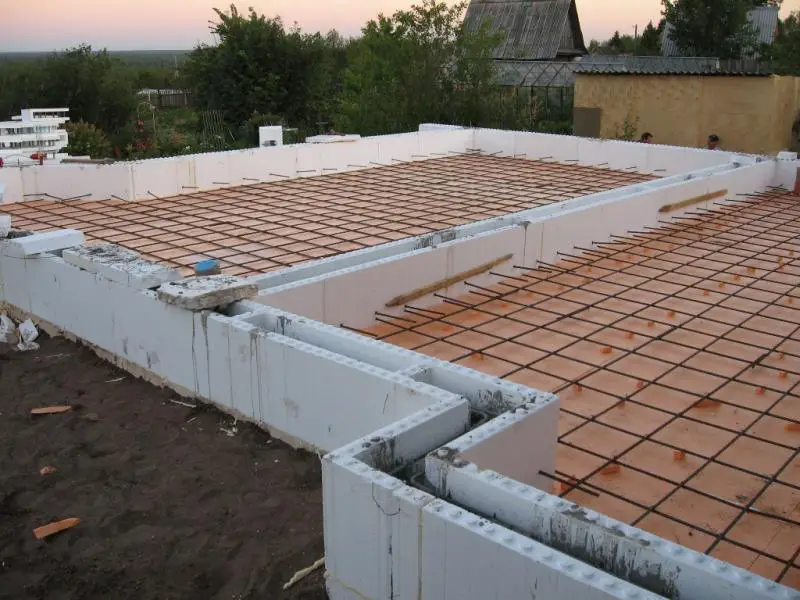
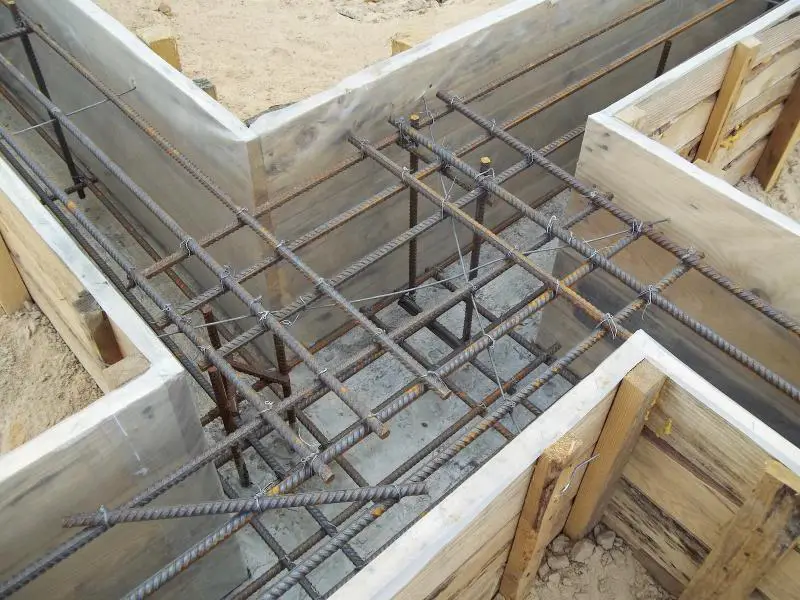
When building foundations, it’s common to use not individual rebar rods, but specially designed rebar mesh manufactured in factories using flattened round steel. A major advantage of foundations built with such mesh is extremely high strength, as the "cellular" rebar mesh contains no welded joints. Welded areas are known to weaken metal strength—this flaw is completely absent in factory-produced "mesh" rebar.
Additionally, in recent years, a new method has become popular: assembling the cellular mesh framework using a specialized pistol that fastens individual rods with steel wire.