There can be your advertisement
300x150
Building a House from Foam Concrete Blocks
Foam concrete blocks are a classic example of construction materials based on lightweight concrete. Their defining characteristic is a porous structure achieved by introducing various foaming additives into the concrete matrix. During autoclave foaming, numerous closed "capsules" filled with air form within the foam concrete block.
Thanks to this, the material's thermal conductivity is reduced, and its thermal insulation properties are significantly improved.
Compared to traditional methods of constructing residential homes from brick or wood, houses built with foam concrete blocks offer several major advantages, the most important of which is construction speed. Large-format lightweight concrete blocks can be quickly assembled by a team of 2–3 workers.

Since foam blocks have relatively high strength but are much lighter than brick or monolithic concrete, there is no need for cranes or heavy lifting equipment during construction. The only exception is unloading material directly from a Euro-freight container onto the site while the blocks are still in factory packaging on pallets.
Several production technologies for foamed concrete blocks allow avoiding the use of harmful chemical components in the raw material formulation. As a result, such homes achieve excellent ecological performance and contribute to creating a healthy indoor microclimate.

Advantages of Building a House from Foam Concrete
The economic benefit of constructing homes from foam concrete stems not only from fast building speed, as mentioned above, but also from several other factors. Below are the main ones.
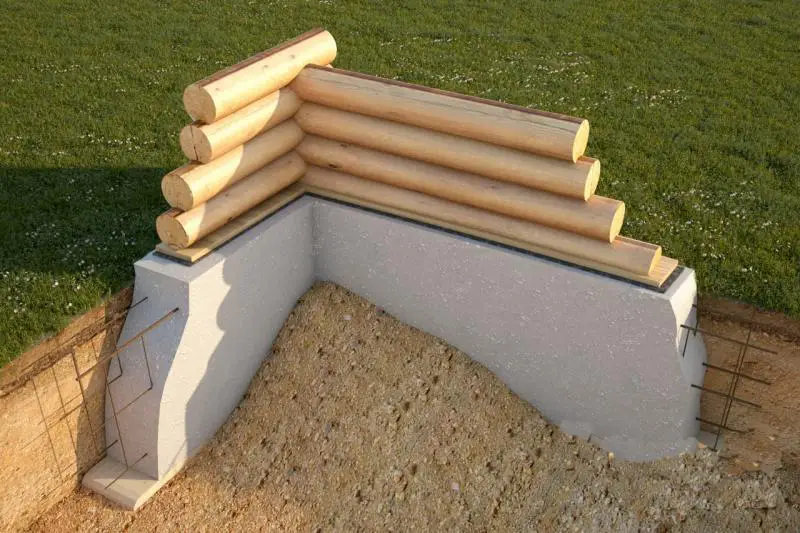
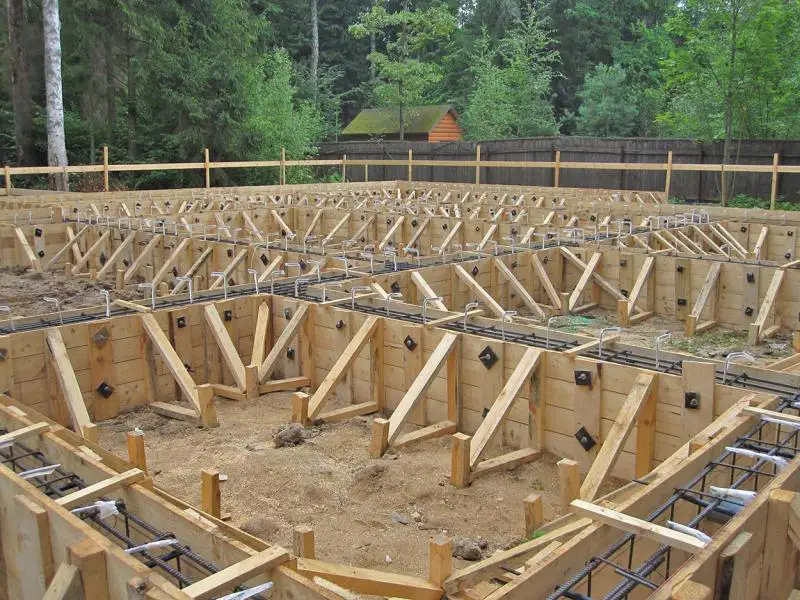
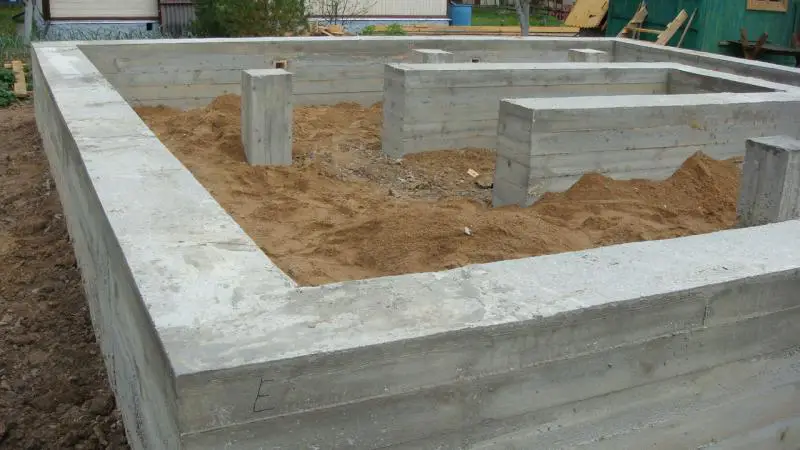
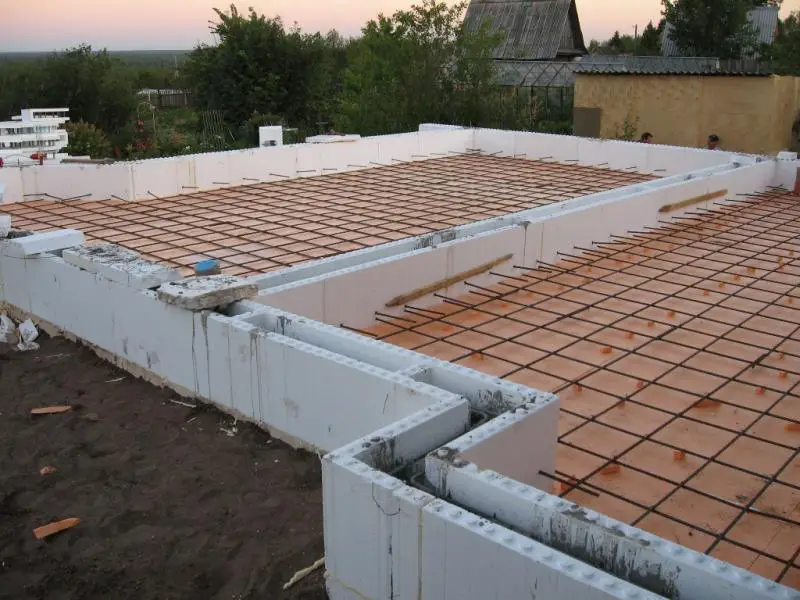
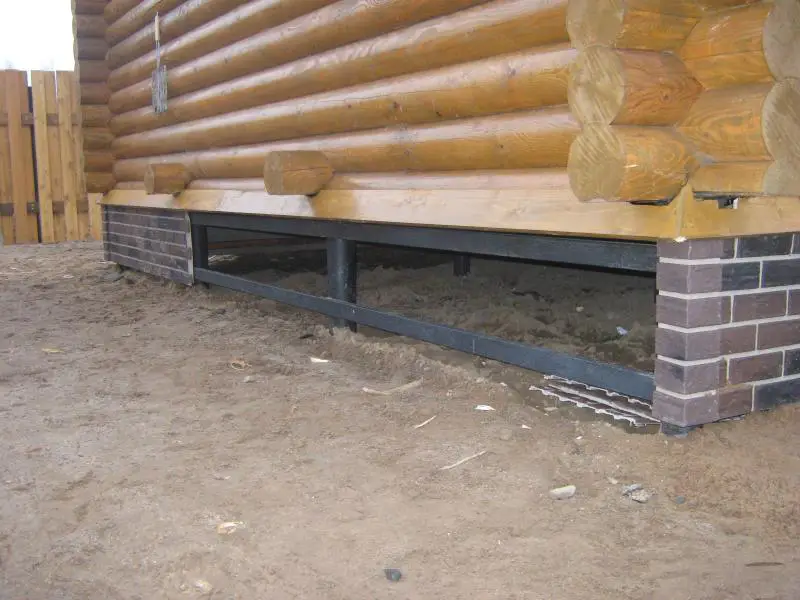
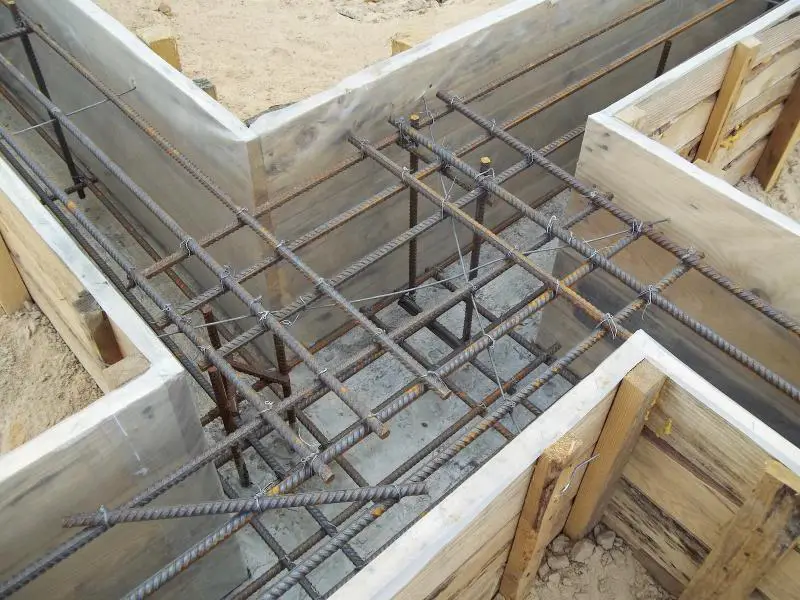
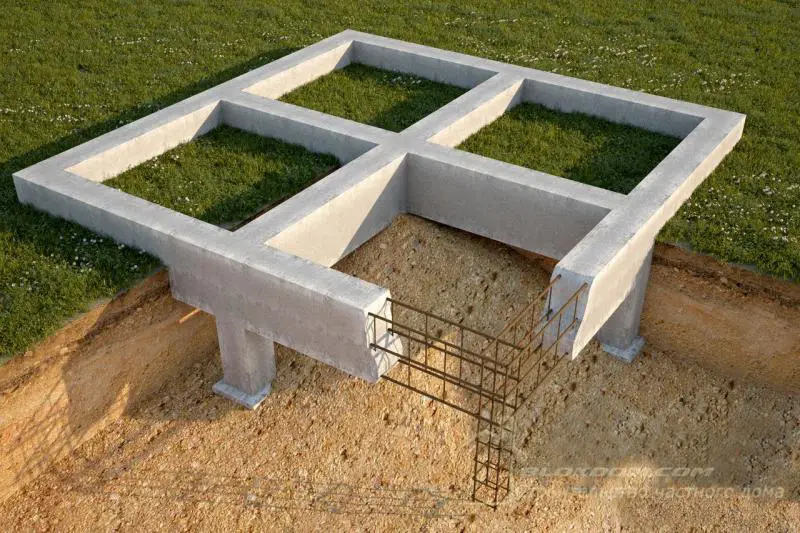
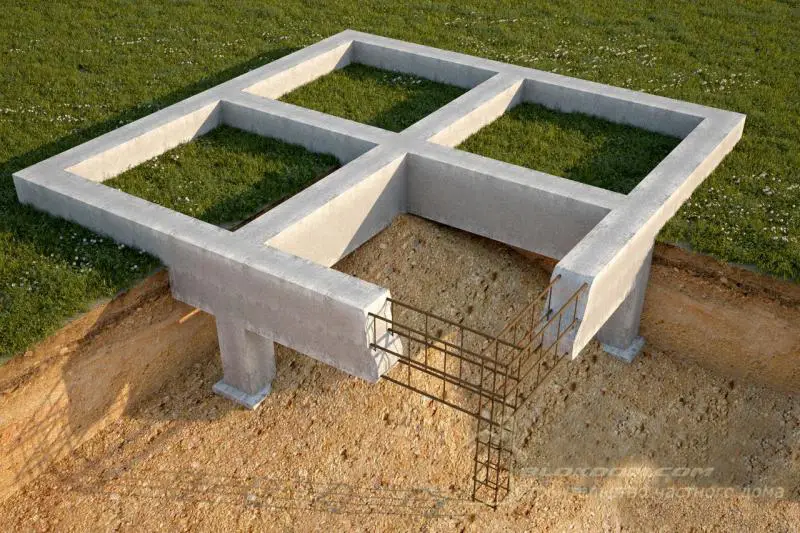
Since foam concrete has a lower bulk density than most traditional building materials, homes made from it impose less load on the foundation. This allows reducing the cross-section of support piles or foundation strips (depending on the foundation type), which in turn reduces concrete and rebar consumption and helps optimize the cost of one of the most expensive parts of a building – the foundation.
The second major advantage of foam concrete is ease of processing and finishing. Contrary to the common belief that block materials are difficult to install, foam concrete blocks are easily cut and can be shaped into various geometric forms.
For example, arches and similar wall elements made from foam concrete are becoming increasingly popular. The material takes plaster well, and its surface is nearly inert to water, ensuring even, efficient application of the plaster layer with minimal thickness.
Hermetically sealed with heat-shrinkable polyethylene film, foam concrete blocks are delivered to the construction site wrapped on pallets. This greatly simplifies unloading, storage, and handling, even in open-site conditions. Packaging is designed to prevent moisture ingress into the block’s matrix and to avoid wetting during storage on the construction site.