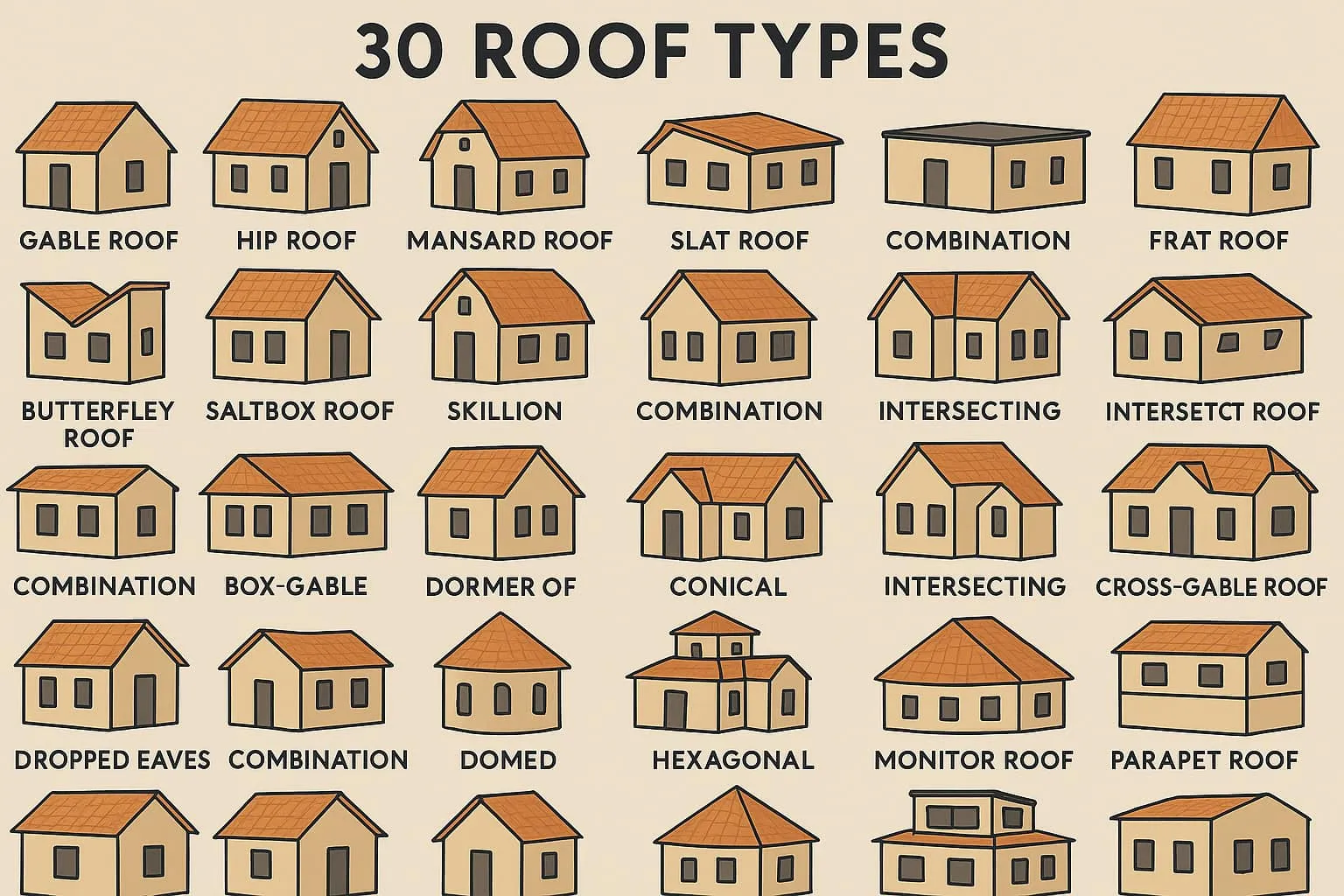
30 Types of Roof Styles for Houses (Popular Designs and Benefits in 2025)
30 Types of House Roofs: A Complete Guide for Homeowners, Builders and Architects
Choosing the perfect roof design is one of the most important decisions you'll make when building or renovating a home. A roof does more than just provide shelter – it affects the energy efficiency of your home, its structural integrity, visual appeal and long-term costs. With so many types of roofs available today, from traditional gable and hip styles to innovative green and butterfly roofs, understanding the pros and cons of each option is vital.
This comprehensive guide breaks down 30 of the most popular types of house roofs, covering key features, benefits, drawbacks and ideal use cases. Whether you're planning modern construction, updating classic housing or seeking sustainable roofing ideas, this guide will help you make informed and thoughtful decisions.
Explore the full list of roof types below, and be sure to check out our detailed comparison table and FAQ section to evaluate costs, durability, maintenance and climate compatibility.
Table of Contents
- 1. Gable Roof
- 2. Hip Roof
- 3. Mansard Roof
- 4. Gambrel Roof
- 5. Flat Roof
- 6. Shed Roof
- 7. Butterfly Roof
- 8. Gable Overhang Roof
- 9. Saltbox Roof
- 10. Jerkinhead Roof
- 11. Skillion Roof
- 12. Dutch Gable Roof
- 13. Dormer Roof
- 14. M-Shape Roof
- 15. Sawtooth Roof
- 16. Pyramid Roof
- 17. Combination Roof
- 18. Crossing Roof
- 19. Curved Roof
- 20. Green Roof
- 21. Front Box Roof
- 22. Clerestory Roof
- 23. Conical Roof
- 24. Crossing Hip Roof
- 25. Crossing Gable Roof
- 26. Dropped Eave Roof
- 27. Dome Roof
- 28. Hexagonal Roof
- 29. Monitor Roof
- 30. Parapet Roof
1. Gable Roof
Description: A gable roof is one of the most recognizable types of roofs, having two sloping sides that meet at a central peak to form a triangular shape. Known for its simple construction and excellent water runoff, it's popular in residential architecture worldwide.
Advantages: Economical, easy to build, excellent for rain and snow drainage, provides ventilation and attic space.
Disadvantages: Weak wind resistance; can be damaged in hurricane-prone areas.
Best For: Cold and moderate climates; suburban homes and cottages.
Gable roofs offer versatility, allowing different roofing materials – from asphalt shingles to metal panels.
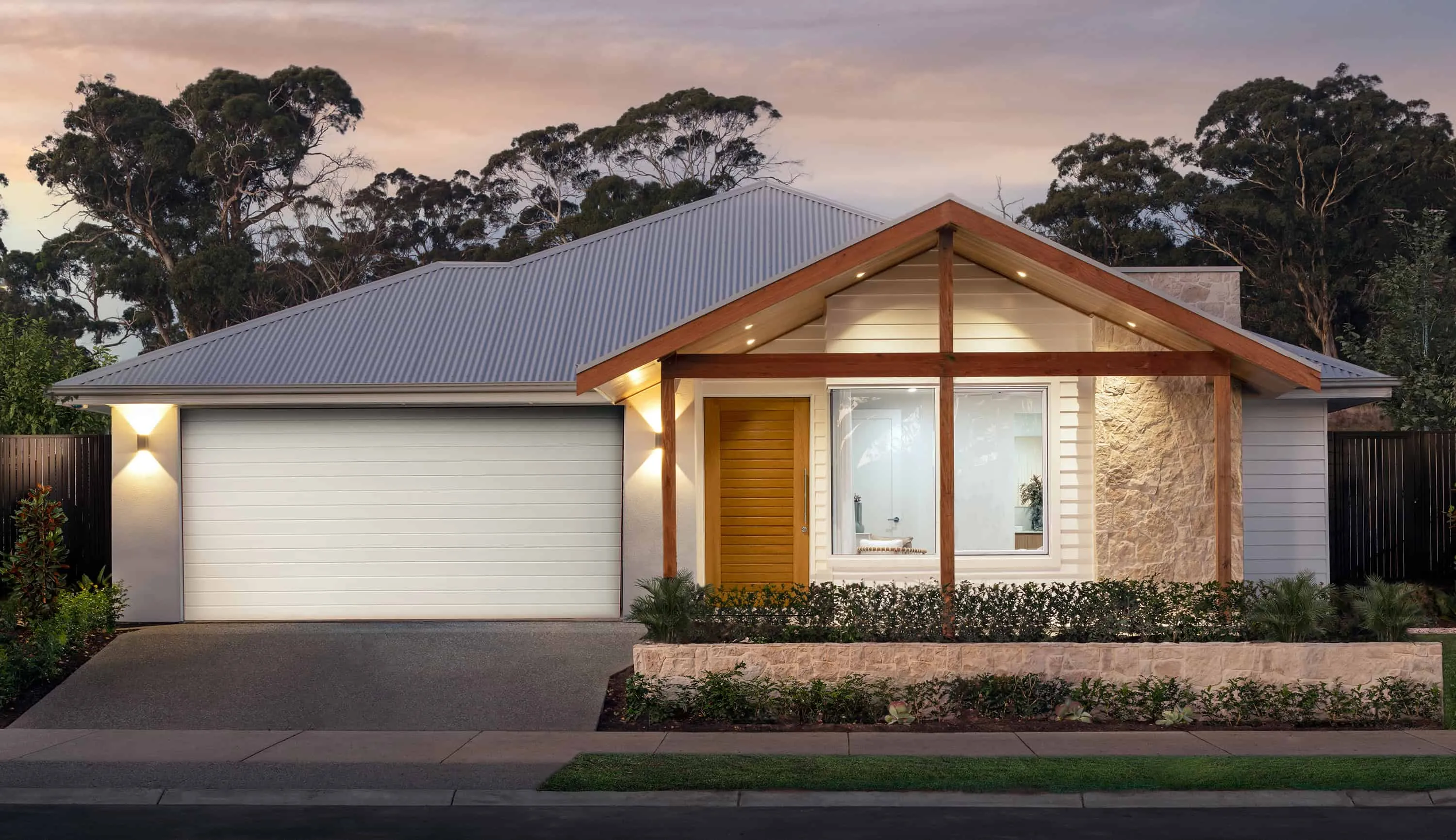 A modern house with a box gable roof, wooden entrance and stone facade wall, combining natural textures with clean architectural lines.
A modern house with a box gable roof, wooden entrance and stone facade wall, combining natural textures with clean architectural lines.2. Hip Roof
Description: A hip roof has slopes on all four sides, converging at a peak to form an edge or point. This type of roof offers greater stability and design balance.
Advantages: Excellent for windy or hurricane-prone areas, stable structure, aesthetically pleasing from all angles.
Disadvantages: More expensive to build, requires more materials and labor.
Best For: Homes in high wind or coastal areas; bungalows and villas.
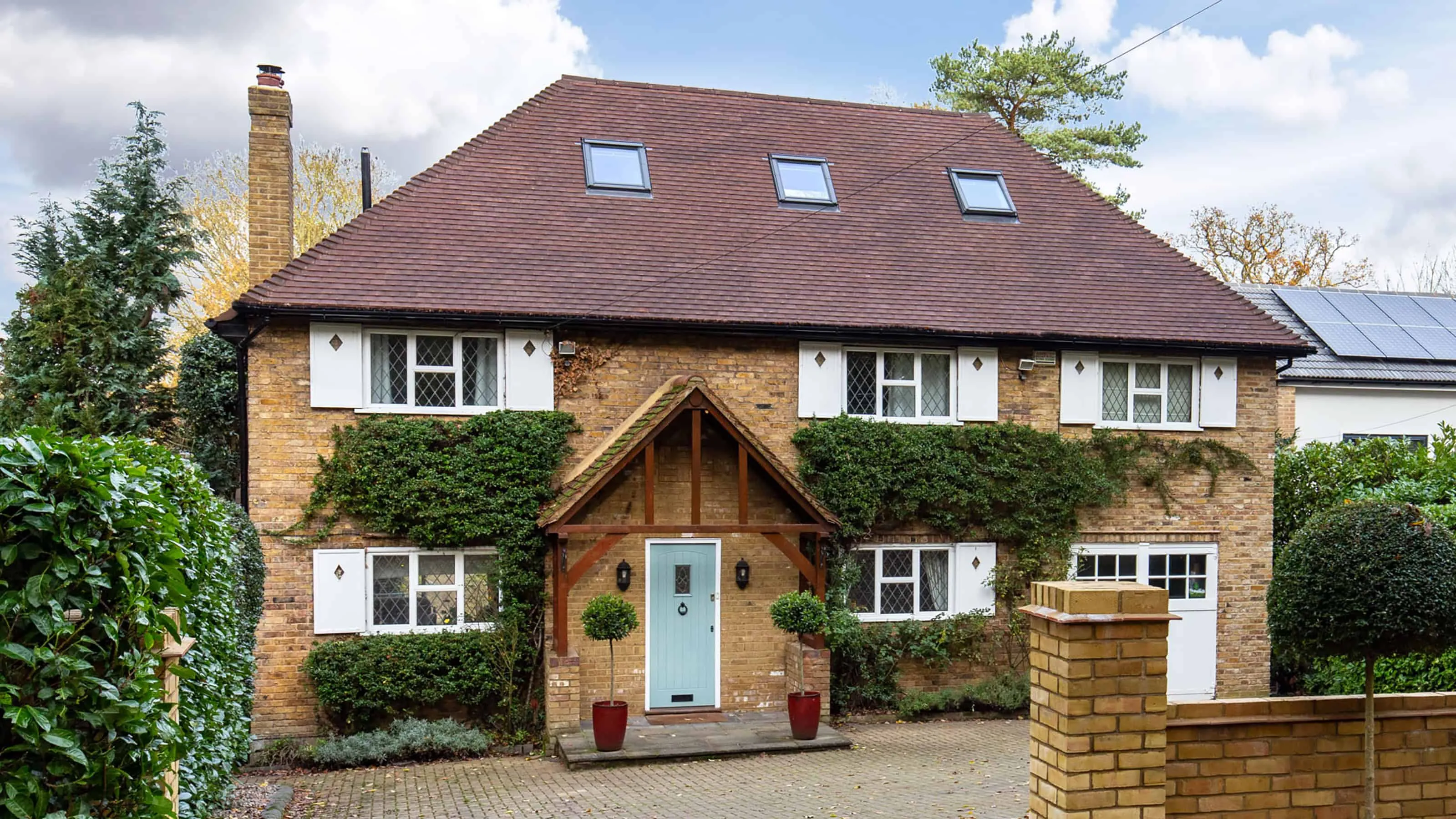 A traditional English house with a hip roof and brick facade, featuring a cozy porch and neat ivy decoration.
A traditional English house with a hip roof and brick facade, featuring a cozy porch and neat ivy decoration.3. Mansard Roof
Description: A mansard roof is one of the most space-efficient types of roofs, featuring a four-sided structure with two slopes on each side – the lower slope is much steeper. This design maximizes attic or upper floor space, making it ideal for urban and historic architecture.
Advantages: Provides extra living space (ideal for lofts or attics), adds aesthetic appeal to historic and classical homes.
Disadvantages: Complex to build and maintain; not suitable for snowy regions due to the steep lower slope.
Best For: Urban homes, historic buildings and French-style architecture.
Due to its steep pitch, a mansard roof often requires premium materials such as slate or synthetic shingles. Learn more in our detailed guide on mansard roof materials.
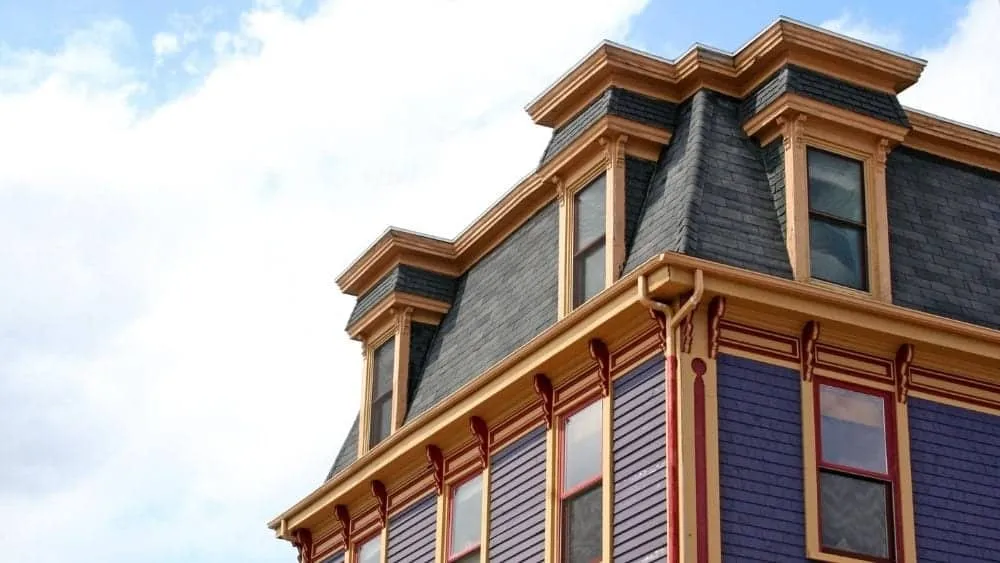 A colorful Victorian house with a mansard roof and decorative eaves, along with vibrant exterior detailing – a hallmark of the 19th century.
A colorful Victorian house with a mansard roof and decorative eaves, along with vibrant exterior detailing – a hallmark of the 19th century.4. Gambrel Roof
Description: A gambrel roof is one of the classic types of roofs, easily recognizable by two different slopes on each side. The steep lower slope maximizes upper-level space, making it a popular choice for barns, lofts and colonial-style homes.
Advantages: Maximizes attic space, economical and attractive for traditional design.
Disadvantages: Less sturdy in high wind or heavy snow areas.
Best For: Farmhouses, barns and homes in Georgian or Dutch colonial style.
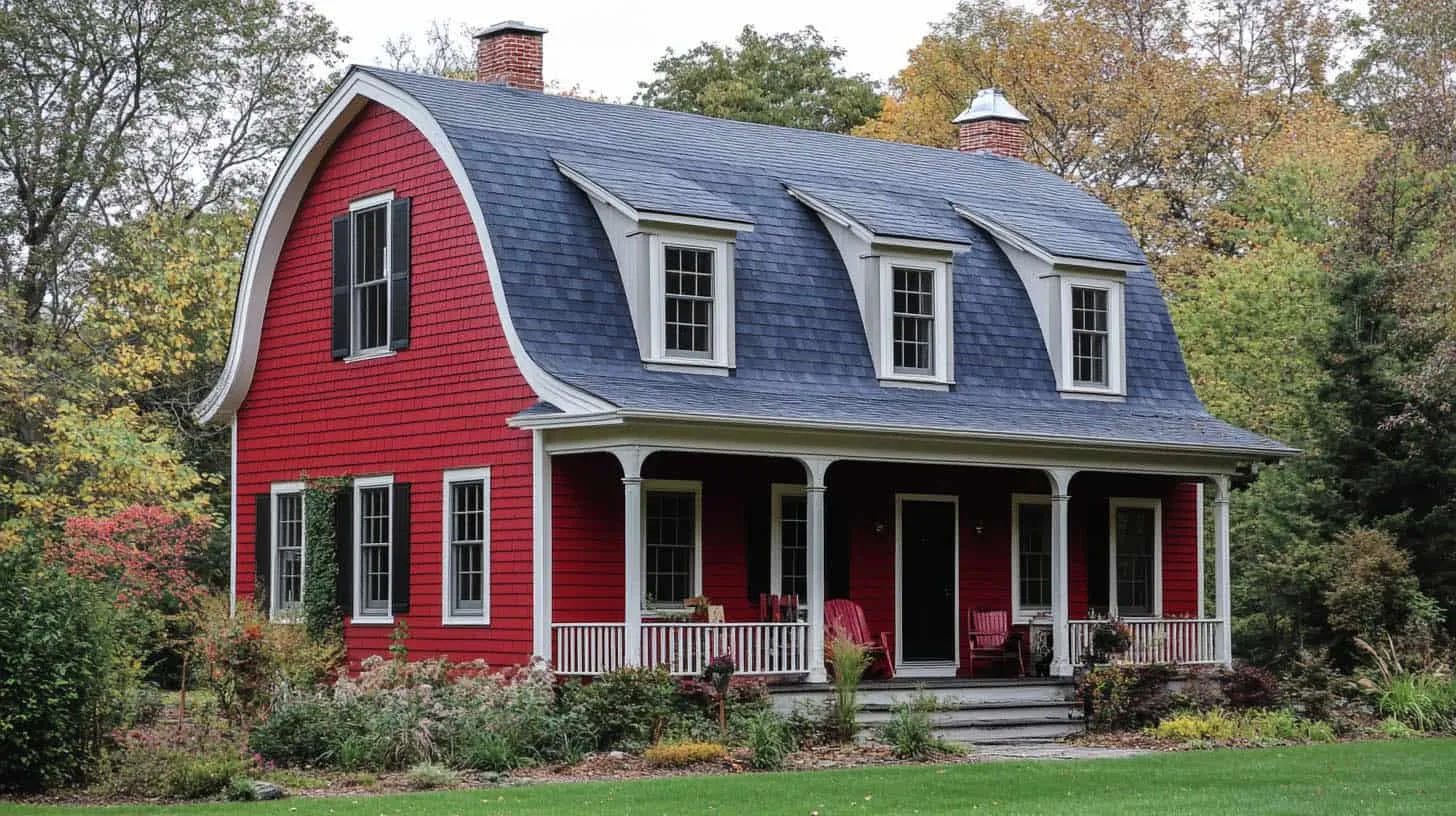 A stunning red house with a gambrel roof, white accents and cozy protected porch – an excellent example of Dutch colonial style.
A stunning red house with a gambrel roof, white accents and cozy protected porch – an excellent example of Dutch colonial style.5. Flat Roof
Description: A flat roof appears smooth but usually has a slight slope for water drainage. It offers a minimalist look and can be used as living or green space.
Advantages: Economical, ideal for terraces or rooftop gardens, easy to build and maintain.
Disadvantages: Prone to water drainage issues and leaks if not properly installed.
Best For: Modern and contemporary homes, urban buildings, warm climates.
Flat roofs are popular in modern and minimalist architecture due to clean lines and functional space utilization. Explore the best materials for flat roofs such as TPO, EPDM and PVC membranes to ensure durability and waterproofing.
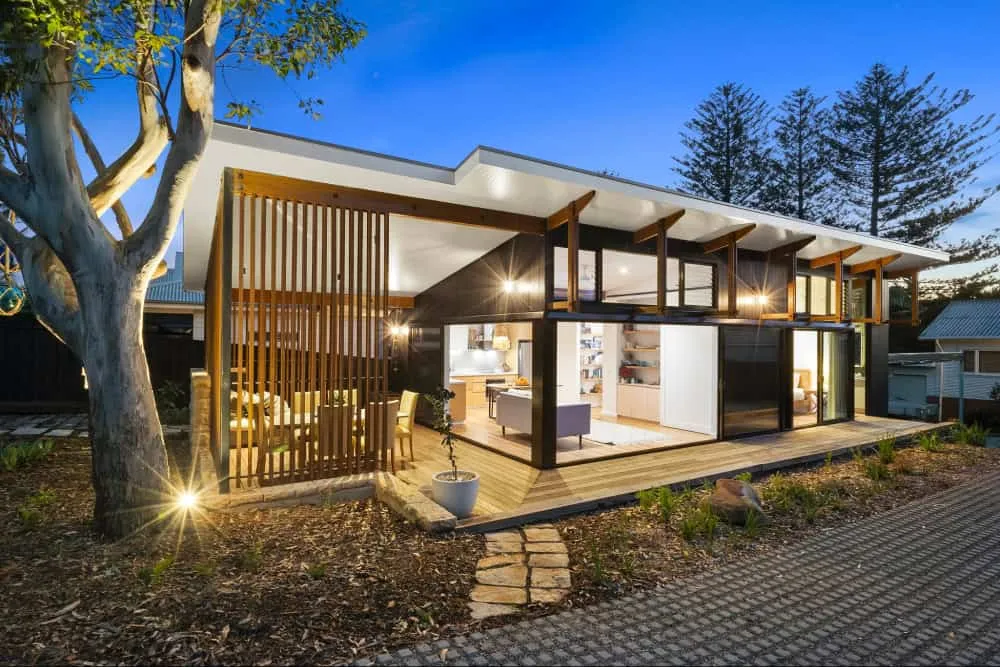 A modern home with an illuminated open living area, large sliding doors and a wooden balcony – perfectly suited for contemporary relaxed lifestyle.
A modern home with an illuminated open living area, large sliding doors and a wooden balcony – perfectly suited for contemporary relaxed lifestyle.6. Shed Roof
Description: Among modern types of roofs, the shed roof, also known as a skillion roof, has one slope in one direction. It is popular in minimalist architecture and home extensions due to clean lines and effective water drainage.
Advantages: Simple structure, promotes water runoff, suitable for solar panels.
Disadvantages: Limited attic space, not ideal for traditional house styles.
Best For: Modern homes, cabins and extensions.
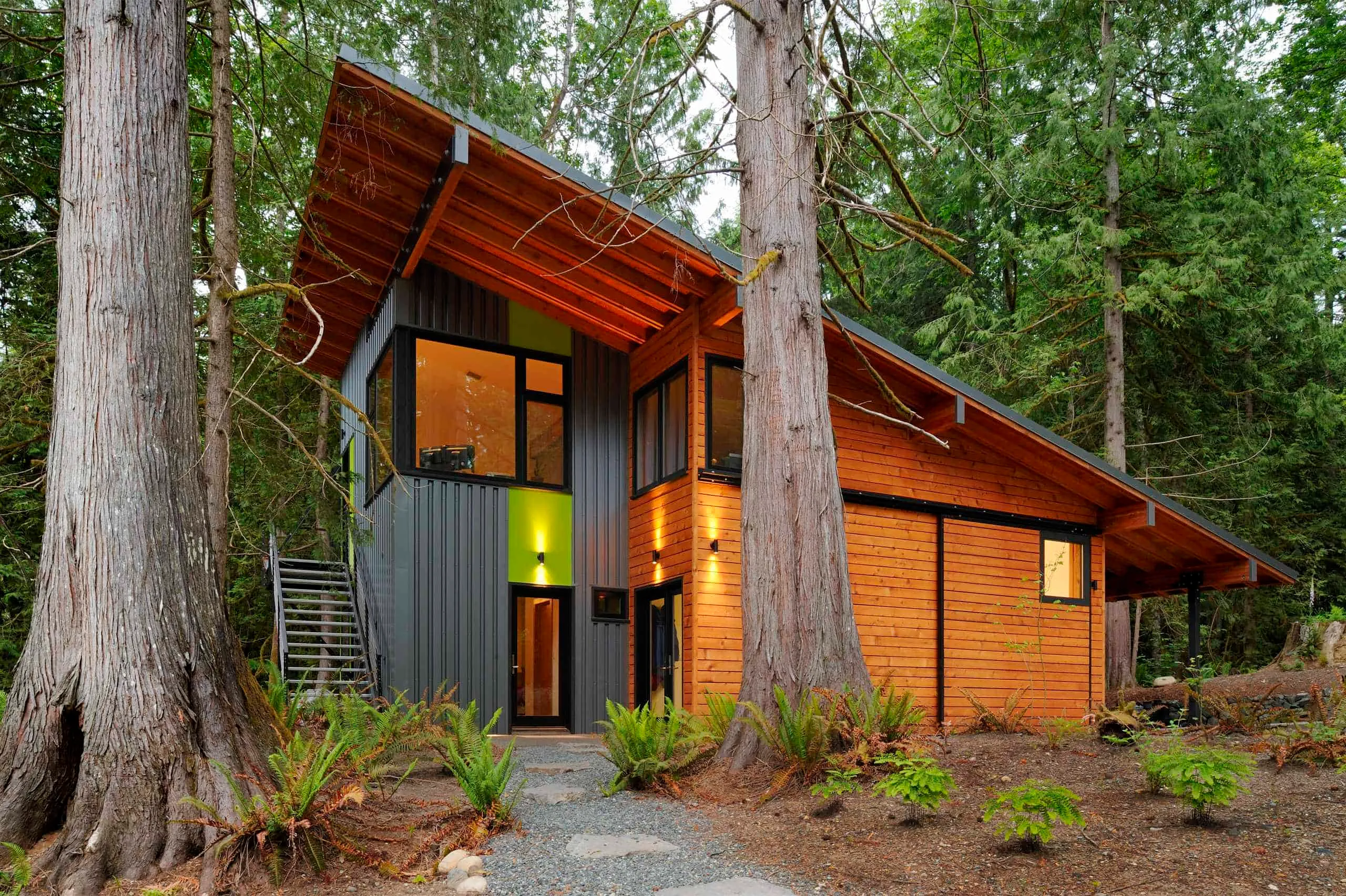 A modern forest cabin with a shed roof and wood-metal facade, designed to harmonize with the rich natural environment.
A modern forest cabin with a shed roof and wood-metal facade, designed to harmonize with the rich natural environment.7. Butterfly Roof
Description: This unique V-shaped roof resembles butterfly wings with two slopes facing inward. It is known for its futuristic appearance and water collection efficiency.
Advantages: Allows for large windows, collects rainwater, supports sustainable design.
Disadvantages: Expensive to build and maintain; may have drainage issues if not properly designed.
Best For: Eco-homes and modern homes in warm climates.
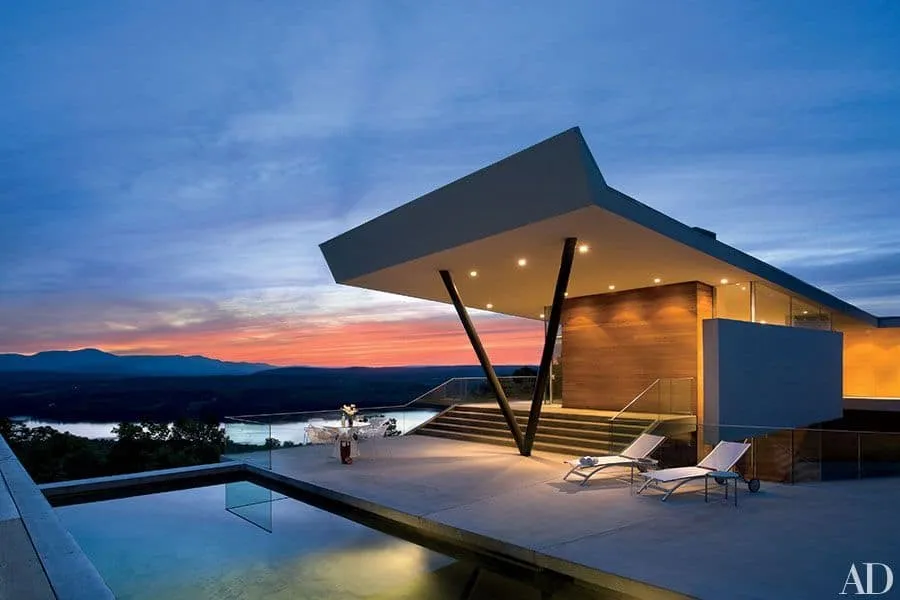 A modern home with a projecting structure over a lake, elegant pool and minimalist design against a dramatic sunset.
A modern home with a projecting structure over a lake, elegant pool and minimalist design against a dramatic sunset.8. Gable Overhang Roof
Description: A gable overhang roof is one of the traditional types of roofs, characterized by double slopes on each side. The lower slope extends forward, creating a protective overhang that provides shade and shelter for terraces or porches.
Advantages: Provides extra shade and protection for outdoor areas; unique architectural appeal.
Disadvantages: Complex and expensive to build; difficult to ventilate.
Best For: Colonial-style homes, homes with terraces and warm tropical climates.
9. Saltbox Roof
Description: A saltbox roof is asymmetrical with a long, steep slope and short slope, giving the house a unique look.
Advantages: Excellent drainage system, wind-resistant, adds character and space to the house.
Disadvantages: Irregular design may limit interior layout flexibility.
Best For: New England style homes, historic restorations and sloped lots.
10. Jerkinhead Roof
Description: As one of the hybrid types of roofs, the Jerkinhead roof, also known as a clipped gable or semi-hip roof, combines features of both gable and hip constructions. Its clipped ends enhance wind resistance, adding a unique architectural profile.
Advantages: Unique appearance, wind-resistant, adds stability to gable structures.
Disadvantages: Slightly more complex and costly to build.
Best For: Craftsman-style homes, Tudor-style houses and windy locations.
11. Skillion Roof
Description: A skillion roof is a single sloped surface, similar to a shed roof but often used as the main roof in modern minimalist homes.
Advantages: Simple and economical to build, excellent water drainage, ideal for solar panel installation.
Disadvantages: Limited attic space; not ideal for traditional house styles.
Best For: Modern energy-efficient homes and extensions.
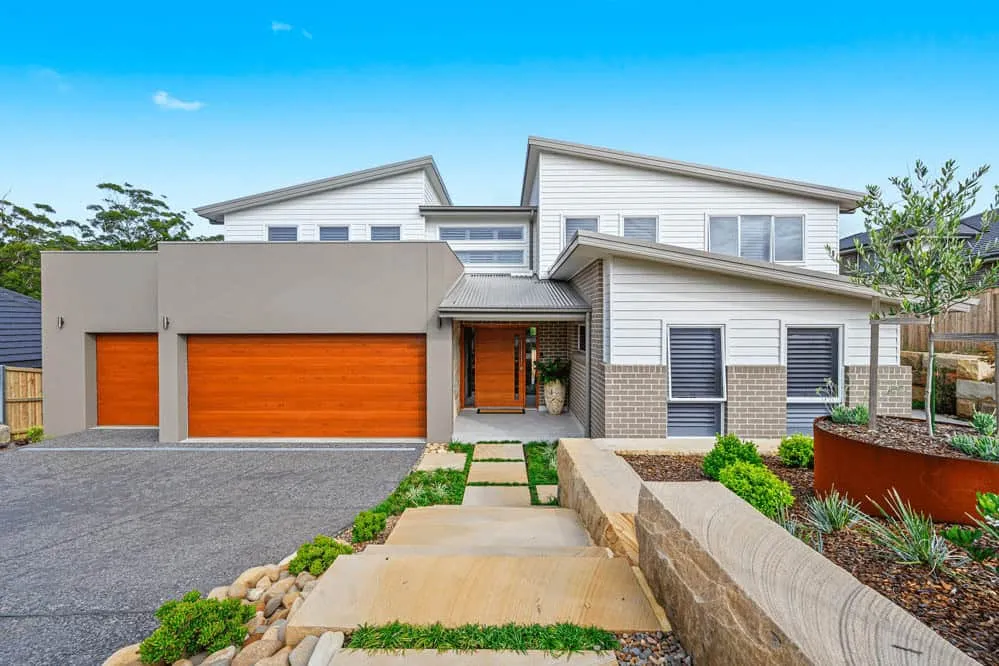 A modern home with intersecting skillion roofs, mixed neutral finishes and bright wooden gates enhancing the exterior look.
A modern home with intersecting skillion roofs, mixed neutral finishes and bright wooden gates enhancing the exterior look.12. Dutch Gable Roof
Description: A hybrid between gable and hip roofs, the Dutch gable roof features a small gable section above a hip structure, combining aesthetics and functionality.
Advantages: Adds extra attic space, improves the home's appearance, enhances ventilation.
Disadvantages: Requires more materials and skilled labor; higher construction cost.
Best For: Suburban homes and traditional homes with large roof spans.
13. Dormer Roof
Description: A dormer is an additional structure protruding from a sloped roof, typically containing a window used to add usable space and natural light.
Advantages: Increases ceiling height, enhances natural lighting, adds visual interest.
Disadvantages: Adds construction costs; potential leaks if not properly sealed.
Best For: Attic conversions, lofts and homes in cold or moderate climates.
14. M-Shape Roof
Description: Among more unique types of roofs, the M-shape roof resembles the letter “M” when viewed from the front, featuring two gable sections connected by a central valley. This design adds architectural interest and allows for sloped ceilings or clerestory windows.
Advantages: Allows for large interior space and many windows, good drainage system.
Disadvantages: Complex to build; valley section requires excellent waterproofing.
Best For: Large homes and modern designs with bold facades.
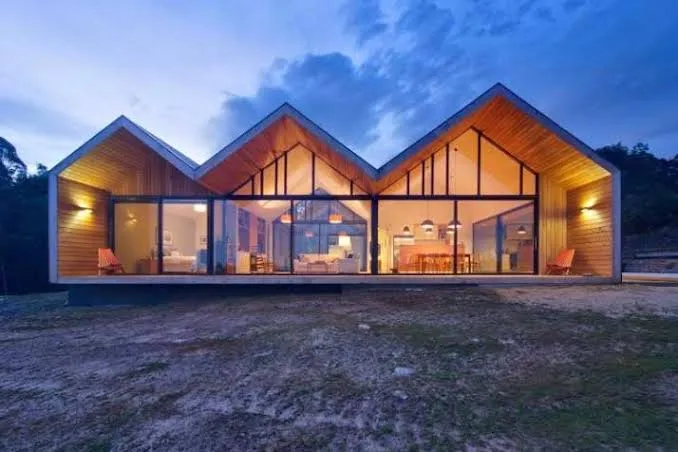 A modern home with an M-shape roof, extended glazing and warm wooden finishes – combining bold architecture with cozy interiors.
A modern home with an M-shape roof, extended glazing and warm wooden finishes – combining bold architecture with cozy interiors.15. Sawtooth Roof
Description: Consists of a series of ridges with double slopes, steeper surfaces are clad in glass to allow natural light penetration.
Advantages: Excellent natural lighting, ideal for solar panels, industrial look.
Disadvantages: High construction cost, difficult to maintain.
Best For: Modern homes, lofts and converted industrial buildings.
16. Pyramid Roof
Description: A type of hip roof where all four sides converge at a single point, forming a pyramidal shape.
Advantages: High wind resistance, symmetrical and visually balanced.
Disadvantages: Limited attic space, not ideal for large buildings.
Best For: Small structures such as gazebos, cabins or compact homes.
17. Combination Roof
Description: A mix of two or more types of roofs used on one structure to create architectural interest and meet functional needs.
Advantages: Customizable to complex floor plans, diverse aesthetic appeal.
Disadvantages: Complex and costly to design; potential leaks at joints.
Best For: Custom homes and eclectic architectural projects.
18. Crossing Roof
Description: Features two or more roof lines intersecting at an angle, often found in homes with multiple wings.
Advantages: Adds depth and dimension, allows for complex floor plans.
Disadvantages: Difficult to build, vulnerable at joints.
Best For: Large residential buildings and traditional homes.
19. Curved Roof
Description: A modern type of roof with a curved shape that softens architectural lines and improves aerodynamics.
Advantages: Excellent modern appearance, ideal for wind drainage, unique aesthetic.
Disadvantages: Requires specialized materials and engineering design.
Best For: Modern, eco-friendly homes and cultural buildings.
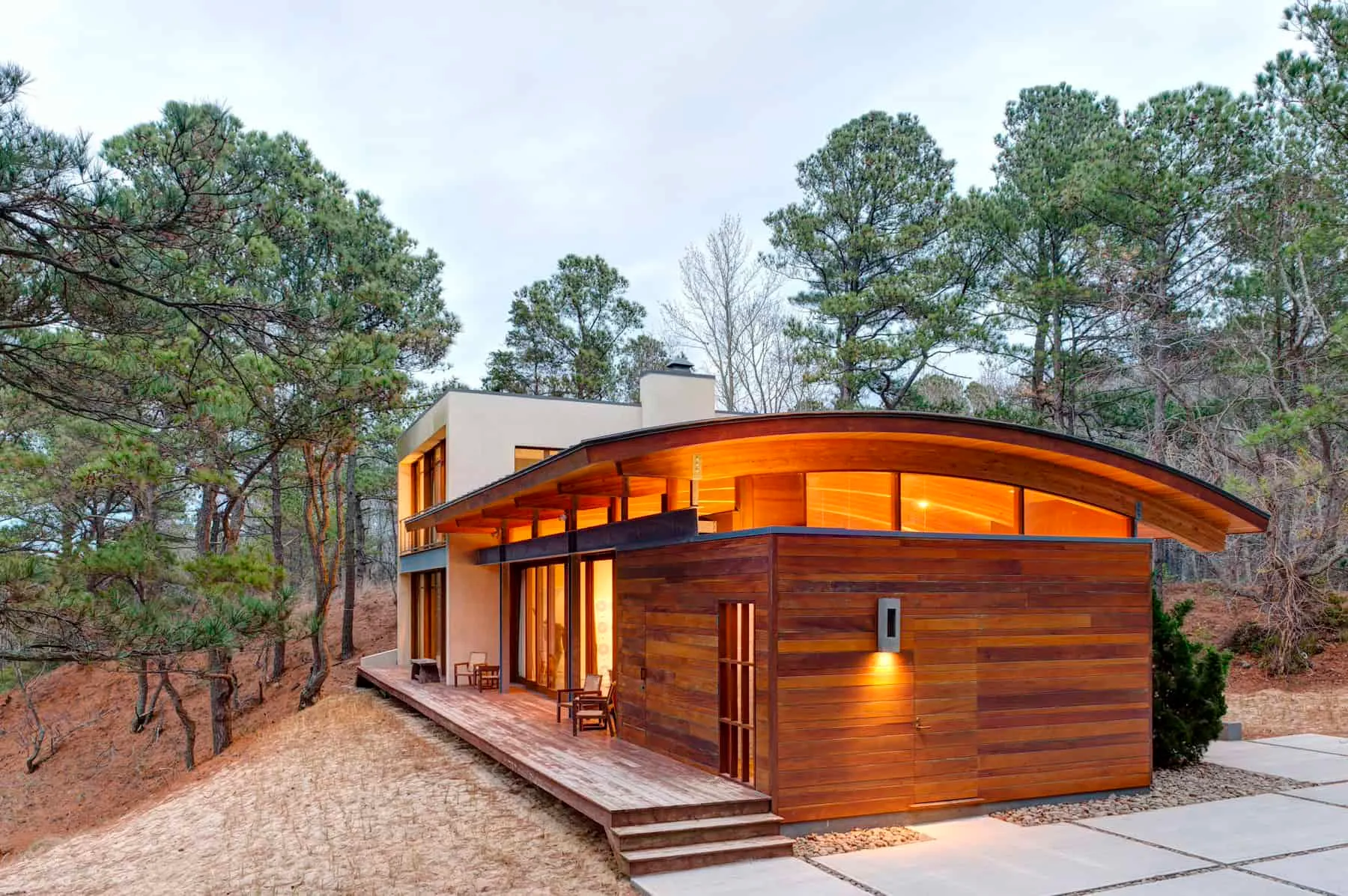 An elegant modern home with an arched roof and wooden facade, located in a peaceful forest setting – combining natural materials with curved design.
An elegant modern home with an arched roof and wooden facade, located in a peaceful forest setting – combining natural materials with curved design.20. Green Roof
Description: Covered with vegetation over a waterproof membrane, green roofs help insulate buildings and manage stormwater.
Advantages: Energy-efficient, eco-friendly, reduces urban heat island effect.
Disadvantages: High installation and maintenance costs, requires structural support.
Best For: Urban rooftops, sustainable homes and commercial buildings.
21. Front Box Roof
Description: Similar to a gable roof but with box eaves on each end for a cleaner appearance.
Advantages: Enhances the home's curb appeal, simple and effective structure.
Disadvantages: May be less wind-resistant in high-wind areas.
Best For: Traditional and colonial-style homes.
22. Clerestory Roof
Description: Features a vertical wall with windows between two sloped roof sections, allowing natural light to penetrate interior spaces.
Advantages: Promotes energy efficiency, ideal for passive solar design.
Disadvantages: Potential heat gain or loss with improper insulation.
Best For: Modern homes and eco-friendly architecture.
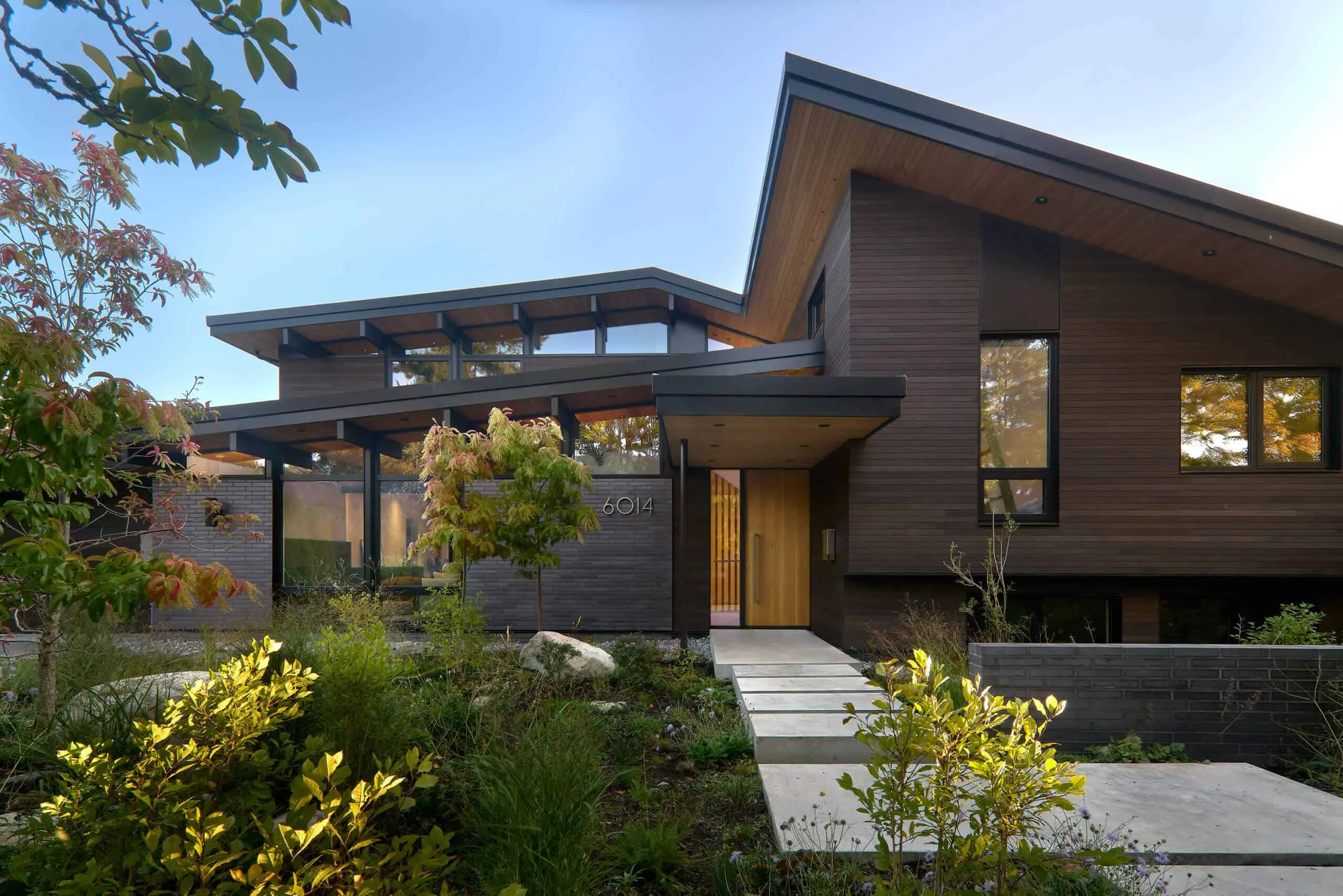 A remarkable modern home with layered shed roofs, clerestory windows and warm horizontal wooden cladding integrated into a landscaped setting.
A remarkable modern home with layered shed roofs, clerestory windows and warm horizontal wooden cladding integrated into a landscaped setting.23. Conical Roof
Description: This type of roof has a circular base that smoothly transitions into a conical shape at the top, often found in towers, pergolas and gazebos. Its unique structure adds charm and elegance to both historic and decorative architecture.
Advantages: Iconic and charming, promotes water runoff.
Disadvantages: Rare and expensive; complex framework construction.
Best For: Historic homes, towers, gazebos.
24. Crossing Hip Roof
Description: A combination of two hip roof sections intersecting, often found in homes with an L or T shape.
Advantages: Good wind resistance, elegant symmetry.
Disadvantages: Complex construction and higher material costs.
Best For: Multi-wing residential buildings.
25. Crossing Gable Roof
Description: Composed of two or more gable roof sections intersecting and forming a cross-shaped plan.
Advantages: Adds volume and visual interest, supports various room layouts.
Disadvantages: Increased chance of leaks where ridges meet.
Best For: Large homes and cottages with complex plans.
26. Dropped Eave Roof
Description: A roof with extended eaves that drop significantly beyond the building edge for additional shade and protection from rain.
Advantages: Excellent for sun and rain protection, improves terrace areas.
Disadvantages: May block views or conflict with minimalist designs.
Best For: Asian-inspired designs, hot or rainy climates.
27. Dome Roof
Description: A semi-spherical roof construction that evenly distributes load and creates a spacious open interior.
Advantages: Structurally strong, energy-efficient, excellent aesthetics.
Disadvantages: High construction cost; rarely used in residential buildings.
Best For: Religious buildings, observatories and unique homes.
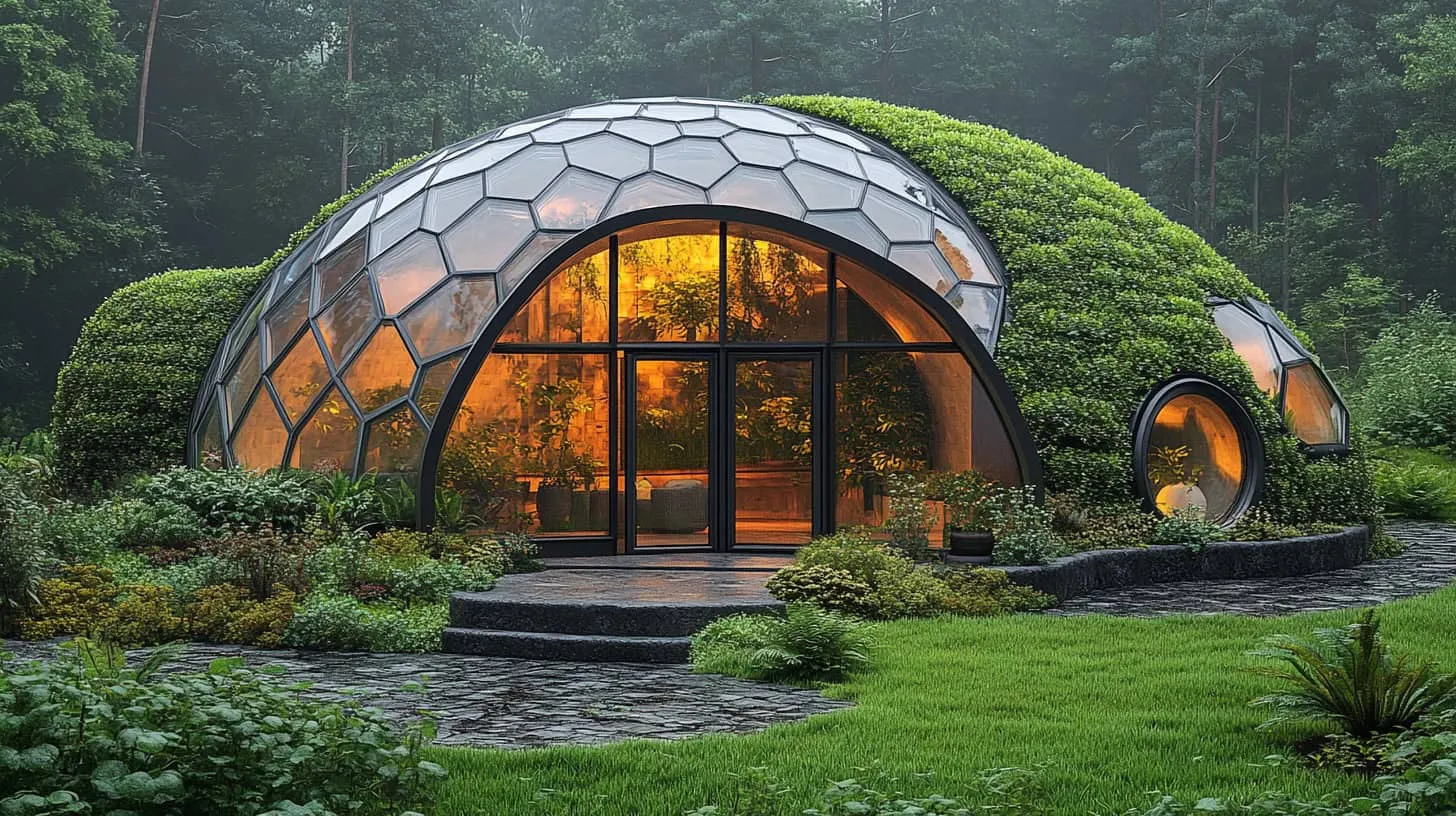 An eco-friendly geodesic dome house with hexagonal glazing and vegetation-covered shell, perfectly integrated into a forest environment.
An eco-friendly geodesic dome house with hexagonal glazing and vegetation-covered shell, perfectly integrated into a forest environment.28. Hexagonal Roof
Description: Built with six sides, this roof is typically used on gazebos or decorative buildings for a visually unique exterior appearance.
Advantages: Attractive, symmetrical and efficient for small structures.
Disadvantages: Limited to smaller buildings; requires precise framing construction.
Best For: Garden structures, gazebos and towers.
29. Monitor Roof
Description: Features a raised central roof section passing along the ridge of a double-sloped roof with clerestory windows for ventilation and lighting.
Advantages: Excellent ventilation and lighting; ideal for barn-style homes.
Disadvantages: More prone to leaks; may require structural support.
Best For: Barns, workshops and industrial or farm-style homes.
30. Parapet Roof
Description: Features a flat roof bounded by a low wall (parapet) that extends beyond the roof, often for safety or aesthetic purposes.
Advantages: Adds architectural interest, hides roof elements, enhances safety.
Disadvantages: Water drainage must be carefully planned.
Best For: Urban homes, commercial buildings and minimalist designs.
Roof Type Comparison: Best Materials, Estimated Cost, Durability, Maintenance and Ideal Climate
Roof Type Best Material Estimated Cost Durability Maintenance Ideal Climate Gable Roof Asphalt shingles, metal panels Low ($4–$9/sq ft) High Low Cold and moderate regions Hip Roof Asphalt shingles, slate, clay tiles Medium ($5–$12/sq ft) High Medium Windy and coastal areas Flat Roof EPDM, TPO, PVC membrane Medium ($6–$10/sq ft) High Low Warm and dry climates Shed Roof (Skillion) Metal sheets, asphalt shingles Low ($4–$8/sq ft) Medium Low Modern and minimalist homes Mansard Roof Slate, copper, composite shingles High ($9–$20/sq ft) High Low Urban and historic areas Gambrel Roof Asphalt shingles, wood shakes Low ($5–$9/sq ft) Medium Medium Rural and colonial areas Butterfly Roof Metal panels, membrane system High ($8–$14/sq ft) High Medium Rainwater collection regions Gable Overhang Roof Asphalt shingles, metal panels Medium ($5–$10/sq ft) Medium Medium Tropical and porch homes Saltbox Roof Asphalt shingles, metal Low ($4–$8/sq ft) High Low Historic and sloped lots Jerkinhead Roof Metal, asphalt, slate Medium ($6–$11/sq ft) High Low Windy and suburban areas Dutch Gable Roof Asphalt shingles, clay tiles High ($7–$13/sq ft) High Medium Traditional and large span homes Dormer Roof Copper, asphalt shingles Medium ($5–$12/sq ft) High Medium Attic conversions and lofts M-Shape Roof Metal panels, membrane systems High ($8–$15/sq ft) Medium Medium Modern and designer homes Sawtooth Roof Corrugated metal, glass panels High ($10–$16/sq ft) High Low Industrial and workshop buildings Pyramid Roof Clay tiles, metal sheets Medium ($7–$15/sq ft) High Low Small cabins and gazebos Combination Roof Mixed materials (metal, tile, asphalt) High ($8–$15/sq ft) High Medium Custom and eclectic projects Curved Roof Copper, zinc, metal panels High ($10–$20/sq ft) High Low Modern and eco-friendly buildings Green Roof Membrane + plant system High ($10–$25/sq ft) Medium High Urban and sustainable projects Clerestory Roof Metal panels, glass inserts Medium ($6–$12/sq ft) High Medium Passive solar and lighting Conical Roof Slate, copper, zinc High ($12–$25/sq ft) Medium Low Towers, pergolas and gazebos Crossing Gable Roof Asphalt shingles, metal Medium ($6–$11/sq ft) High Low Complex floor plan homes Dropped Eave Roof Metal sheets, polycarbonate Medium ($5–$10/sq ft) Medium Low Hot and rainy climates Dome Roof Concrete, metal, fiberglass High ($12–$25/sq ft) High Low Unique and monumental structures Hexagonal Roof Wood shakes, metal sheets High ($4–$9/sq ft) Medium Low Garden pavilions and small towers Monitor Roof Metal panels, clerestory glass Medium ($7–$12/sq ft) High Medium Barns and workshop homes Parapet Roof Concrete, TPO or PVC membrane High ($8–$14/sq ft) Medium Low Urban and minimalist designs*Estimated costs are based on average residential data from 2025 and may vary depending on location, materials and roof complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Roof Types
Which roof types are most economical?
For budget-conscious homeowners, gable roofs and shed roofs (skillion) are among the most affordable types of roofing. Their simple construction and low material usage make them ideal for economical building.
Which roof styles offer the best energy efficiency?
Green roofs lead in insulation and temperature regulation, while clerestory roof designs enhance natural lighting and support passive solar heating, reducing overall energy consumption.
Which roof types are best for snowy climates?
Roofs with steep slopes, such as gable, mansard and saltbox roofs, are most effective in regions with heavy snowfall. These designs efficiently shed snow, minimizing accumulation and structural load.
Which roof designs work best in high wind or hurricane zones?
Aerodynamic roof types, such as hip and pyramid roofs, are recommended for storm-prone areas due to their excellent wind resistance and structural strength.
What is the average lifespan of various roof types?
Standard roofs, such as gable or hip styles with asphalt shingles, can last 20–30 years. Premium options like metal roofs or slate tiles used on curved or dome roofs can exceed 50 years with proper maintenance.
Can flat roofs be used in rainy or snowy climates?
Flat roofs can be used in such climates if equipped with quality membranes and an effective drainage system. However, sloped roof types are generally preferred in areas with frequent rain or snow.
What maintenance is required for green roof types?
Green roofs require seasonal maintenance such as weeding, watering and regular inspection of the waterproof layer. Maintenance needs depend on plant selection and climate.
How do I determine the best pitch for my roof type?
Pitch depends on climate and architectural goals. Steep pitches (above 6:12) are ideal for rain and snow runoff, while flat and low-pitch roofs suit dry regions and modern homes.
What factors affect roof replacement costs?
Key cost indicators include roof size, materials (asphalt vs. tile or metal), design complexity (gable vs. crossing roof), labor costs and structural repair needs.
Which roof types are most sustainable for urban homes?
Among eco-friendly roof types, green roofs, solar panels on shed roofs and butterfly roofs for water collection are excellent choices for sustainable urban living.
Which roof types add the most value when selling a home?
Architecturally appealing and durable roof types – such as hip, mansard and metal gable roofs – can enhance curb appeal and property value due to their longevity and low maintenance.
More articles:
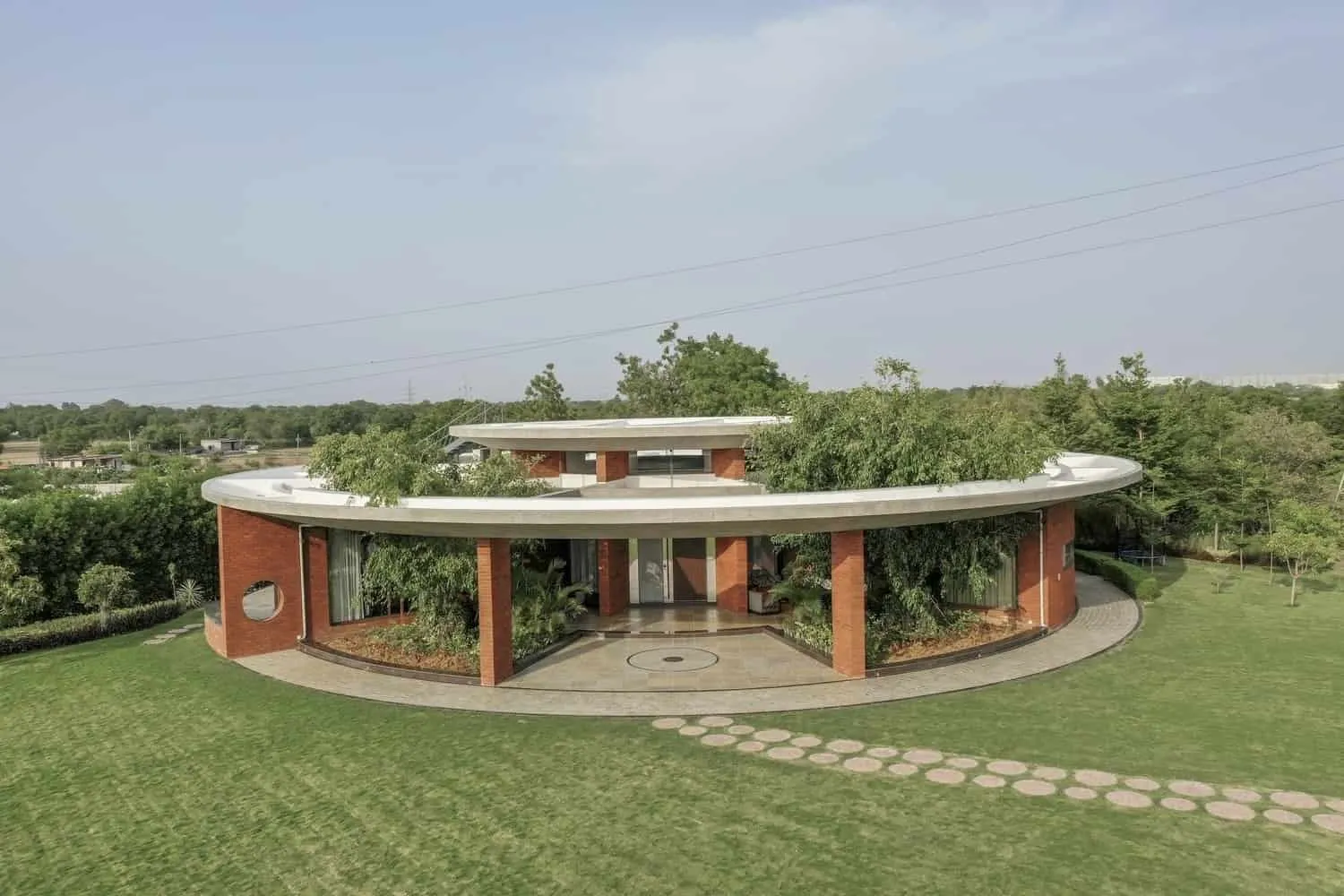 Round House by studio prAcademics in India
Round House by studio prAcademics in India Growth of Simple and Functional Bedrooms in 2024
Growth of Simple and Functional Bedrooms in 2024 The Rise of Cotton Gauze in Modern Bedding Accessories
The Rise of Cotton Gauze in Modern Bedding Accessories Restoring the Trend of Vanity Tables in Modern Bathrooms: Beauty Returns to Contemporary Spaces
Restoring the Trend of Vanity Tables in Modern Bathrooms: Beauty Returns to Contemporary Spaces Rise of Barn Dorms: A Modern Approach to Rural Housing
Rise of Barn Dorms: A Modern Approach to Rural Housing The Ritz-Carlton Residences by SAOTA: A New Standard in Aegean Coastal Living
The Ritz-Carlton Residences by SAOTA: A New Standard in Aegean Coastal Living The Role of Rollers and Guides in Garage Door Operation
The Role of Rollers and Guides in Garage Door Operation The Role of Contactless Water Heaters in Modern Home Design
The Role of Contactless Water Heaters in Modern Home Design